Describe the General Structure of an Amino Acid
Amino acids are the basic components of proteins. This atom is surrounded by three chemical groups.

General Structural Formula Of Amino Acids Where R Can Be H Ch 3 Download Scientific Diagram
Acetyl coenzyme A is a pyrophosphorylated derivative of a pantothenic acid amide.

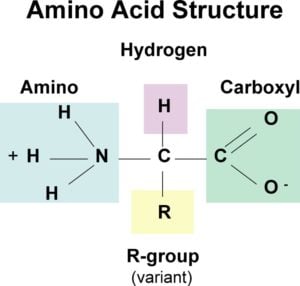
. Amino acids are known to contain amine and carboxyl functional groups. In the centre of the amino acid is an assymetric carbon atom called the alpha carbon. The carbon atom of the carboxyl group has a free bond.
It is a component of pantothenic acid HOCH 2 C CH 3 2 CH OHCONHCH 2 CH 2 CO 2 H a member of the vitamin B complex and an essential nutrient. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Structure of Amino Acids.
Describe the various levels of protein structure primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The amino group in beta-alanine has moved to the end of the three-carbon chain.
A water molecule is removed by releasing an OH from carboxyl group of one amino acid and hydrogen from the amino group of another amino acid. The general structure of Amino acids is H2NCH RCOOH and it can be written as. Two amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to build up proteins.
Although the neutrally-charged structure is commonly written it is inaccurate because the acidic COOH and basic NH 2 groups react with one another to form an internal salt called a. Basic Structure of an Amino Acid. The simplest and smallest amino acid found in proteins is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen H.
The primary structure of a purine is two carbon-nitrogen rings. Start studying General structure of Amino acid. The R-group or side-chain varies among the 20 amino acids.
They also contain a side chain that is made up of an R-group where R can denote any alkyl or aryl group. 20 rows Amino acids are molecules used to build proteins. These R-groups are what differentiate amino acids and are responsible for their unique properties.
Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and. All amino acids have the same basic structure shown in Figure 21. First week only 499.
Describe the basic structures of tRNAs. Amino acids are a type of organic acid that contains both a carboxyl group COOH and an amino group NH 2. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the and attached to it are four groups a hydrogen a carboxylic acid group an amine group and an R-group sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain.
A polypeptide folds into a 3D structure called a protein. Amino acids are monomers or building blocks that bind together into peptides. There are 20 different amino acids and they all share the same general structure.
The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid. Each of these basic carbon-nitrogen rings has different functional groups attached to it. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
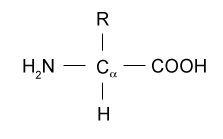
All amino acids follow a general structure known as a general formula of amino acids. COOH H2N C H R. Cytosine thymine and uracil are classified as pyrimidines which have a single carbon-nitrogen ring as their primary structure Figure 1.
Amino acids are classified using their specific R groups. The general structure of Amino acids is H2NCH RCOOH and it can be written as. General Structure of Common Amino Acids General structure of amino acids group and a variable side chain Side chain determines.
All amino acids contain a carbon atom in the middle of the molecule the alpha-carbon. Biology questions and answers. One is an amine group -NH 2.
This is the variable radical group and is different for every amino acid. How are amino acids linked together to form proteins. All amino acids found in proteins have this basic structure differing only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain.
They are all made up of the same amine-carbon-acid combination with a variable side chain. All amino acids have a central carbon atom. The α carbon carboxylic acid and amino groups are common to all amino acids so the R.
Describe the basic structure of amino acids and how the peptide bond forms between amino acids. The general formula for an amino acid is given below. State the different levels of protein structure and describe how they relate to function.
This carbon is covalently bonded to. An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. Amino acids are comprised of an amine a carbon backbone and an acid.
The third group is denoted by R. A molecule that contains an amino functional group is called an amine. Scientists use the name amino acid because these acids contain both amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their basic structure.
This R group makes the amino acid unique. The amino acids in a protein are bonded to each other with peptide bonds - hence the term for a polymer of amino acids is a polypeptide. Amino acids are the monomers that comprise polypeptides polypeptides being the polymers.
The second one is a carboxyl group -OOOH. Explain how alternative splicing generates different proteins with similar but not identical functions 4. Start your trial now.
Protein folding binding to specific ligand and interaction with its environment Amino acids consists of a constant COOH R is side chain At neutral pH H 2 N- protonated to H 3 N- and COOH deprotonated to COO-. 1Describe the basic structure of an amino acid. Solution for Describe the basic general structure of an l-a-amino acidand draw its structure.
These contain one hydrogen atom one amine group -NH 2 one carboxylic acid group -COOH and one side chain R group attached to the central carbon atom. According to this formula each amino acid consists of A carboxylic group -COOH. He amino acids are regarded as building blocks of proteins.
An a-amino acid except proline has an amino group -NH2 a carboxyl group -COOH a hydrogen atom -H and a side chain -R group bonded covalently to a central alpha-carbon atom. Organic substances containing both amino and carboxylic groups are known as amino acids. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids and all have common structural features an amino group -NH3 a carboxylate -COO- group and a.
On the basis of their chemical nature and structure the 20 standard amino acids have been grouped classified as follows-. Terms in this set 16. There are twenty amino acids.
Structure of Amino Acids. Any carbon atom other than that of the carboxyl COOH.
Amino Acids Definition Properties Structure Classification Functions

Amino Acids Structure Classification Properties With Videos Examples

Amino Acids Structure Optical Activity And Classifications Microbiology Notes
No comments for "Describe the General Structure of an Amino Acid"
Post a Comment